My recent post on Herts Memories, Hertfordshire’s community archive network hosted by Hertfordshire Archives and Local History (HALS).
Tag: Mulhausen
At the frontiers of tourism
On 17 September 1888 the Pall Mall Gazette of London declared: ‘ “Boycott Mulhausen and take up with Delle” should be the tourists’ Plan of Campaign’. This surprising rallying cry had been sparked by a recent unfortunate incident at Mülhausen (known as Mulhouse in French) on the Alsace-Swiss border.
Charles Seale Hayne, Liberal MP for Ashburton in Devon, had chosen to travel from Belfort, just north of Delle, on the German Imperial Railways in Alsace Lorraine, via Mülhausen to Basle in Switzerland. The problem was he didn’t have a passport. The Gazette explained that because of the recently introduced ‘vexatious passport regulations’ in Alsace, he was refused entry and detained at Mülhausen by German authorities. Expressing scant sympathy for Mr Seale Hayne, the Gazette remarked that it had been ‘pointed out over and over again for the benefit of English tourists that there were two lines from Belfort to Basle, one of which does, and the other of which does not, pass through German territory … he ought to have gone by the Franco-Swiss one’. They went on to note acidly that, in the matter of coming a cropper when you’ve broken the rules, ‘Members of Parliament must not expect to be safer than other individuals’. How topical that sounds!

Alsace and Lorraine had been French but were ceded to Germany at the end of the Franco–Prussian war in 1871. Since then they had been a flashpoint in an escalating war of nerves between the two countries, which was punctuated by periodic outbursts of megaphone diplomacy. The new ‘vexatious’ passport rules were the latest act in this long-running drama. Germany was experiencing some domestic drama at the time as well: a few days after the new passport rules came into force, on 1 June 1888, it acquired a new Emperor – Kaiser Wilhelm Ⅱ.
The regulations in question proclaimed that any foreigner entering Alsace–Lorraine from France required a passport, with accompanying visa from the German embassy. For those wishing to travel to Basle there was an alternative route via the French railway company, La Compagnie des Chemins de fer de l’Est, which avoided crossing into German territory and didn’t need a passport. This explains the Pall Mall Gazette‘s sensible advice to tourists.

Passports were something of a novelty at this period. In fact, as the UK National Archives’ study guide points out, ‘[b]efore the First World War it was not compulsory for someone travelling abroad to apply for a passport. Possession of a passport was confined largely to merchants and diplomats, and the vast majority of those travelling overseas had no formal documents’. So these new rules represented a significant, and expensive, inconvenience for anyone wishing to travel through France into Alsace–Lorraine.
By the middle of the 19th century there were increasing numbers of British tourists keen to explore Alsace, especially the Vosges mountains which attracted exponents of the relatively new pastime of mountain climbing, or alpinism as it was known. Initially mountaineering was the preserve of the English upper class, who had been pioneers of this gentlemanly sport. In 1865 a group of young climbers, including three Englishmen, became the first to reach the summit of the Matterhorn in Switzerland. Tragically, they became even more famous for the controversial accident on their descent which killed several of the party, including Lord Francis Douglas. By the close of the century the monied middle classes were also venturing into the mountains in greater numbers and local hotels and restaurants were quick to capitalize on the growth in foreign tourism.
As well as being a trying inconvenience for prosperous tourists, the passport regulations threatened to make daily life for ordinary frontaliers – those who lived and worked in the border area between France and Alsace – a source of constant aggravation. There was much bad press in France and Britain about the heavy-handedness of German passport officials. The Yorkshire Evening Press of 5 June 1888 repeated a French newspaper report that German authorities had prevented some French army veterans who lived in Alsace from returning home after their regular trips across the border to France to receive their pension payments.
But there are hints that in practice the regulations quickly became honoured more in the breach than in the observance. The St James’s Gazette of 1 October 1890 featured an account of two British tourists ‘bent on a tramp among the hills of Alsace’. Having duly armed themselves with the required visas from the German embassy in London, they found that they didn’t need them once during their ten-day excursion, even though they had crossed and re-crossed the France–Alsace border many times. In fact they each greatly regretted the ten shillings they had shelled out for their visas. To encourage fellow tourists to consider sampling the delights of ‘this truly beautiful holiday-ground’ the writer helpfully detailed the sort of typical, mouth-watering lunch that travellers could expect at a local Alsatian inn: ‘excellent soup, iced salmon with mayonnaise sauce, fillet of beef with potatoes … veal cooked as only foreigners can cook it, with meringues and cream and cheese to follow’. All for less than four shillings apiece, including a bottle of ‘fair’ wine. It’s hard to imagine anyone tramping much further than their hotel room for une sieste after consuming that meal!
Eventually the difficulties for locals and tourists alike, not to mention political pressure, led to the passport regulations being officially revoked on 1 October 1891. But the experience had helped to keep alive the question of Alsace and Lorraine’s status as German territories and there were increasing calls for their restoration to France. The issue was by no means straightforward. By the late 1890s nearly 30 years had passed since these areas had become part of the German Empire and a new generation had grown up knowing nothing else. In 1898 a British newspaper reported the impressions of another tourist, recently returned from a ‘long holiday sojourn in Alsace and Lorraine’. He was convinced that most of the younger population were quite happy with their lot and observed that nothing ‘a succession of French Governments have done since 1871, including their dealings with Dreyfus, is calculated to inspire the Lorraine breast with a desire to be again under its control’.

The reference to the Dreyfus affair was very topical and it had local significance for Alsatians. Alfred Dreyfus had been born into a Jewish family in Mulhouse in 1859, before the area was ceded to Germany and became known as Mülhausen. He had subsequently become a cavalry officer in the French army and was wrongly convicted of spying for the German Empire by a secret court martial in 1895, then sentenced to life imprisonment on Devil’s Island in French Guiana. His case became an international cause célèbre. Emile Zola famously addressed his open letter to the President of the French Republic in defence of Dreyfus, J’accuse, in which he denounced the military establishment as anti-Semitic. Alfred Dreyfus had to wait until 1906 before being completely exonerated. The actual spy was later revealed to be Charles Marie Ferdinand Walsin Esterhazy who escaped to Britain and died in Harpenden in Hertfordshire in 1923.
Some of this turmoil and paranoia about spies and foreigners can be detected in the French censuses. Up to 1881 they did not record the nationality of householders, but from 1886 onwards they did. For residents of a town like Delle – next to the borders with Switzerland and the rest of Alsace – this emphasis on stating your nationality might have felt vaguely threatening, especially as many of them had probably been born in parts of Alsace now in the German Empire. For historians and family researchers, however, it could offer some insight into how diverse the population was.
The census data from Delle between 1886 and 1911 record a steady increase in the number of households and persons enumerated although, curiously, the number of households seemed to increase at a faster rate than the number of inhabited buildings. This was especially so between 1891 and 1896. Could this mean that there was a shortage of housing? It would be interesting to discover if this was because of particular local conditions or if it simply mirrored a national trend.
I’ll explore more records from Delle in my next post.
In another country
The past is a foreign country: they do things differently there.
L P Hartley
On Sunday 1 August 1914, a 56 year old English businessman hurried from his accommodation in Rixheim, a suburb of Mülhausen in Alsace, toting a heavy case and in search of transport home. He was in the middle of a business trip and had been monitoring the worsening political situation in Europe for several days, during which time ‘letters to England were returned to us, no telegrams were permitted, and the local telephone was disconnected’. By Sunday he had resolved to leave. If he’d delayed, he would have found himself in the middle of one of the first engagements of the First World War on the Western Front: the Battle of Mülhausen.
I found a contemporary newspaper account of this intrepid Edwardian’s dramatic journey back to Blighty in a microfilm collection at Hertfordshire Archives and Local History Studies (HALS). The British Newspaper Archive (BNA), while being a truly wonderful resource, doesn’t have every newspaper, and for some titles it only has copies from certain years in their collection. It’s always worth checking in your local county archives to see if they have newspapers not covered by the BNA. After some further research online I was able to discover quite a lot more about this gentleman’s life and his connection to Alsace, which helped explain what he was doing there in the first place. I’m planning to explore this in a future post, or possibly an article.
Intrigued by his story, I was keen to learn more about Alsace, with its history of shifting borders and a population regularly rendered ‘foreign’ at a stroke. So I thought I’d take a look at census returns from this area for the period just before the outbreak of the 1914-18 war.
The 2021 census of all parts of the United Kingdom took place on 21 March. The 100-year time limit for the release of records from the 1921 census is also nearly upon us. From 6 January 2022 historians, genealogists, and family history enthusiasts will be able to consult the records from England and Wales on Findmypast.
The information recorded by early censuses in the UK was limited – for example the 1801 census was mainly concerned with gathering regional and national data on the number and size of households across the country – and the details were not considered important, most being destroyed. The sorts of questions posed in the census can in themselves be revealing insights into society at the time, as no doubt will be the questions in the 2021 census. All of this provides fascinating grist to the mill of historians.
Borderland
If, according to L P Hartley’s 1953 novel, The Go-between, the past is virtually a foreign country, how much more ‘foreign’ might the past of a completely different country be? France began conducting national censuses (recensements) every five years from 1801 and I thought it would be interesting to look at returns from the 1911 one, since this is also the latest year for which historic UK census records are currently available.
The commune of Delle, in the département of the Haut Rhin in eastern France, came under the administrative territory of Belfort, which had historically been part of Alsace. The 1870 treaty which ended the Franco-Prussian war saw Belfort carved out of Alsace to remain in France, while the rest of the region was subsumed into the German Empire. Maps of the period show Delle in its French enclave, bordered by the rest of Alsace on one side and Switzerland on another.
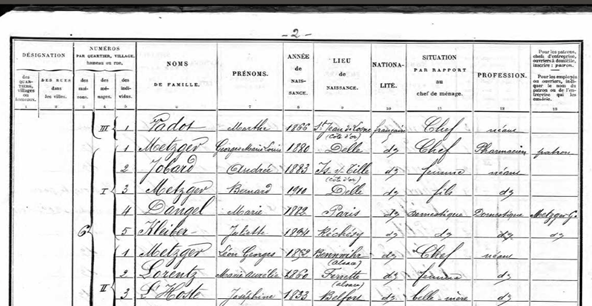
According to the census of that year, Delle’s population in 1911 amounted to 2627 individuals. A quick glance at the records reveals an interesting aspect of the French census which differs from the UK censuses of the period: married women were listed by their maiden names, not their married names. In the example below we see that the wife of farmer Célestin Schmitt is Marie Daucours.

That sort of detail could be gold dust to a family historian and might help, along with Marie’s recorded year of birth (année de naissance) and birthplace (lieu de naissance), to locate a marriage record for the couple and an earlier birth record for Marie. However, as most family researchers know, life isn’t always straightforward and in practice it’s often difficult to find records in archives if the information hasn’t been name indexed or, even better, digitized. Marie was born in Switzerland and unfortunately only some Swiss births, marriages, and deaths records (otherwise known as BMD) are available online; FamilySearch and Ancestry have some collections but they are incomplete.
By contrast, online BMD collections for England and Wales, Scotland, and Ireland are far more complete; but locating a married woman in a 1911 UK census return wouldn’t necessarily make it easy to find other records for her, because only her married name would be recorded in the census. So to uncover her maiden name might involve quite a lot of frustrating extra work.
In general, however, the treatment of married women in the censuses of both countries at this time is similar: they imply that, by definition, they didn’t do anything worth noting. Under the heading profession in the French census the word néant (meaning none) was recorded for the majority of married or widowed women, as it is for Marie Daucours above. In the UK censuses this column was commonly just left blank for married women. This is a classic example of how a census can reveal something about the society performing it even when it leaves things out!
In the Delle census of 1911 there are some intriguing exceptions to this rule. Marie Weber, the 38-year-old wife of locksmith Charles Jacob, is recorded as running her own grocery and haberdashery business. The last column in the census form was where the enumerator noted details of a person’s employer. The words patron for a man or, less commonly, patronne for a woman, indicated that the person owned their own business.

Further down the page we find Fanny Roussey, the 66-year-old wife of François Frémeaux. François is a few years older than Fanny and has no recorded occupation, but she works as a day labourer (journalière), probably doing manual work of some kind.


The mention divers in column thirteen means that Fanny works for more than one employer, possibly local farmers. To be engaged in that kind of hard, physical work at her age, Fanny is what the French might call une femme courageuse!
In some cases, it’s easy to estimate what a married woman was actually doing from the context of the household. For example, the Delle census return lists Mathilde Emma Cuenin, wife of the wonderfully-named Swiss hotelier Clovis Henri Maître. Although Mathilde’s occupation is recorded as néant, she was very probably closely involved in running the hotel, given that it employed her sister as a maid and her husband’s two brothers as waiters. On the other hand, it’s just possible that she sat around all day eating Swiss chocolates while the rest of the family busied themselves with useful tasks. We’ll never know.
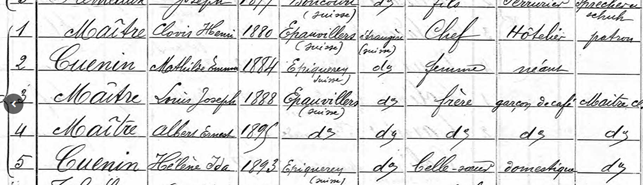
From this cursory look at the census returns we start to get a picture – however hazy – of the population of Delle in the period just before the First World War. So far, we can deduce that it had enough agriculture to support jobbing labourers and was large enough for small businesses to establish themselves – and that it had at least one hotel. Some of the population appear to have been born over the border in Switzerland.
In my next post I’ll continue to explore records from Delle to try to flesh out this sketch.



